Recycling Symbols and Their Meanings: Your Basic Recycling Guide
When it comes to recycling, knowing what items to recycle and how to recycle them can be confusing. Understanding what different recycling symbols mean makes it easier for you to properly dispose of different materials. We’re breaking down the most commonly used recycling symbols to make your recycling experience easier.
In many countries, including the United States and the European Union, some regulations require businesses to label their products with recycling symbols to ensure proper disposal. By using the correct symbols, businesses can comply with these regulations and avoid potential fines or penalties. We’re breaking down the most commonly used recycling symbols to make your recycling experience easier.
Avoid the Confusion: Clarifying Recycling Symbols
The recycling symbol can be misleading in a few different ways. Let’s get these misconceptions out of the way first:
- Not all materials with the recycling symbol are recyclable. Just because an item has a recycling symbol does not necessarily mean that it can be recycled in your area. Make sure to check with your local recycling facility to find out what materials they accept.
- The recycling symbol doesn’t represent the entire recyclability of an item. A product may be made of multiple materials, only some of which are recyclable. Take a plastic water bottle: if it has a metal cap, the cap may not be recyclable.
- The recycling symbol doesn’t indicate a product’s environmental impact. Just because an item is recyclable doesn’t automatically make it environmentally friendly or sustainable. For example, certain products made from recycled materials may still have a large environmental impact due to the energy required to recycle them.
Keep these considerations in mind when reviewing recycling symbols on items you’re disposing of, and when in doubt, do your own research to make informed environmental decisions. To ensure that you’re recycling correctly, it’s best to check with your local recycling program to see which materials are accepted for recycling in your area. You can also look for specific recycling instructions on the product packaging or visit the manufacturer’s website for information on recycling their products.
The 6 Most Common Recycling Symbols
Here are some common recycling symbols and what they mean:
1. The Mobius Loop (Chasing Arrows)
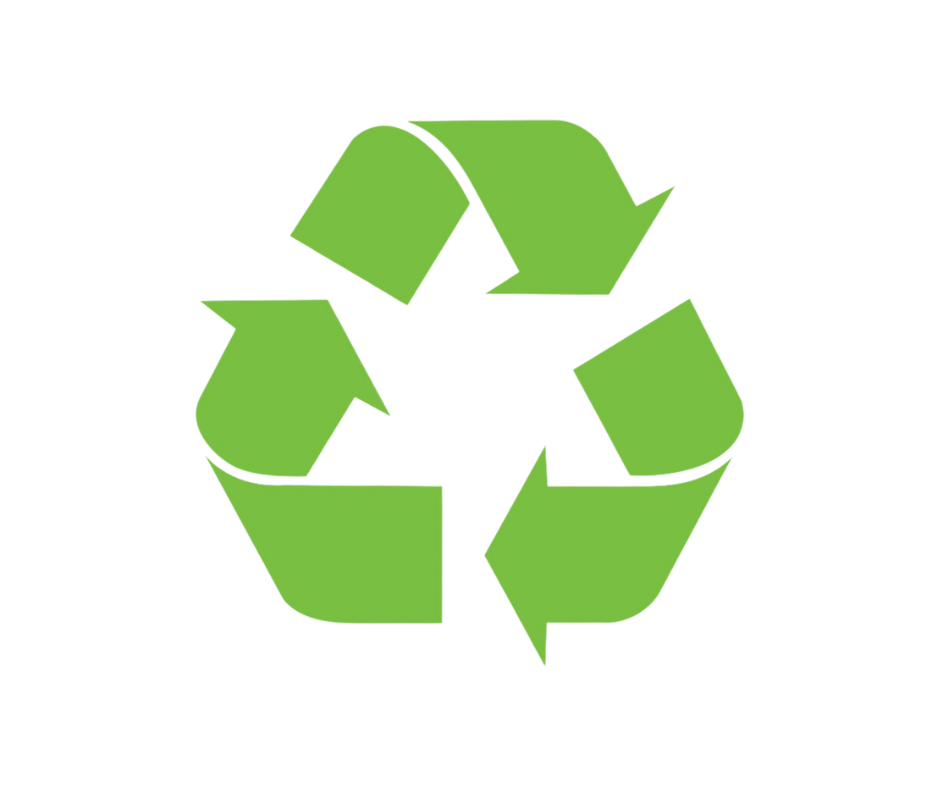

The most well-known recycling symbol indicates that a material is generally recyclable.
What is the Mobius Loop?
The symbol indicates that a product or packaging material is recyclable but it doesn’t guarantee that the product or packaging material will be recycled. The Mobius Loop symbol, also known as the recycling symbol, consists of three arrows in the shape of a triangle. Types of Recyclable Material Under Mobius Loop include:
- Paper– Paper products such as cardboard boxes, paper bags, and newspapers.
- Glass –Glass bottles, jars, and other glass packaging.
- Metal– Aluminum cans, steel cans, and other metal packaging.
- Textiles– Clothing, fabrics, and other textile materials.
- Plastics–Different plastic waste, but will also include a number.
What is the number inside the loop?
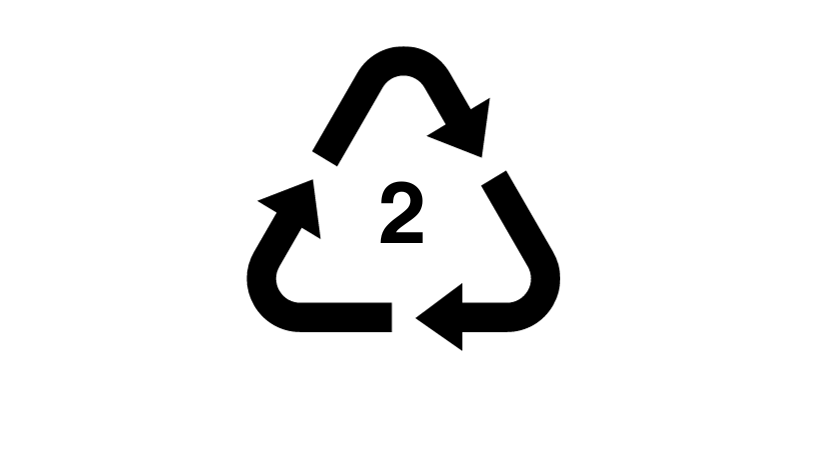
The number inside the arrows refers to the specific type of plastic used in the item, with 1 being the most common and 7 being the least common. The numbers inside the recycling symbol are called a Plastic Resin Code. Plastic resin codes, also known as resin identification codes (RIC), are a set of symbols used to identify the type of plastic material in a product or packaging. Typically found on the bottom of plastic containers, these codes are useful for recycling and sorting purposes. Here are the most common plastic resin codes and their corresponding plastic types:
- PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate):
– Commonly used for soda bottles, water bottles, and food packaging. - HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene):
– Found in milk jugs, detergent bottles, shampoo bottles, and many types of plastic bags. - PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride):
– Used in pipes, vinyl siding, and some plastic wrap. It is not as commonly used for consumer packaging due to environmental concerns. - LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene):
– Often used in grocery bags, some food packaging, and squeezable bottles. - PP (Polypropylene):
– Found in yogurt containers, bottle caps, medicine bottles, and various food containers. - PS (Polystyrene):
– Used for disposable plates, cups, and packaging materials like foam peanuts. - Other Plastics:
– This category encompasses any plastic resin that doesn’t fall into the above categories, including various types of less common plastics.
It’s important to note that while these resin codes provide information about the type of plastic, they don’t necessarily indicate whether a plastic item is recyclable in your area. Recycling guidelines can vary by location, so it’s essential to check with your local recycling program to determine which plastics they accept for recycling. Additionally, some plastics with the “Other” code (7) may not be easily recyclable, and their recycling options can be limited. The acceptance of materials for recycling may vary depending on local regulations, the availability of recycling facilities, and the specific requirements of the recycling program.
2. The “Green Dot” Symbol

Importance of The Green Dot Symbol
Understanding the Green Dot symbol and its significance is important for businesses that manufacture and distribute products in Europe, or for those who export products to European markets. By displaying the Green Dot symbol on packaging, manufacturers show that they are taking responsibility for the packaging waste generated by their products and are contributing to the recovery and recycling of that waste. This can be an important factor in meeting legal requirements for recycling and waste reduction in Europe, as well as in building a positive reputation for environmental responsibility.
This symbol tells us that a product is part of a product stewardship program, which means that the manufacturer is taking responsibility for the environmental impact of the product throughout its lifecycle. This isn’t specifically related to recycling, but instead demonstrates the manufacturer’s commitment to sustainable production.
What is the Green Dot Recycling symbol?
The Green Dot symbol indicates that the manufacturer of the product has paid a fee to a packaging recovery organization in order to contribute to the costs of recovering and recycling packaging materials. The Green Dot symbol is a recycling logo that is commonly used in Europe. It was created by a non-profit organization called Duales System Deutschland (DSD) in Germany in 1991.
The Green Dot symbol is used to indicate that the product’s packaging is part of a collection and recovery system for packaging waste. The symbol is often found on packaging such as paper, cardboard, plastic, and metal.
3. The “Compost” Symbol

This symbol indicates that a material is biodegradable and can be composted. If your household or organization has a composting practice, you can add the item to your compost bin.
What does the Compost Recycling Symbol mean?
The compost symbol is a logo that is used to indicate that a product or material is compostable. The symbol features a stylized leaf with the word “compostable” written underneath it. The compost symbol is intended to help consumers identify products that are suitable for composting and to help composting facilities identify materials that can be composted.
The compost symbol is used on products that meet specific standards for compostability. These standards may vary depending on the country or region but generally include criteria for biodegradability, toxicity, and the ability to break down into usable compost. In many cases, products that are certified as compostable have been tested in composting facilities to ensure that they break down properly and do not leave any harmful residues behind.
Types of Compostable Material
There are many types of organic material that can be broken down into nutrient-rich soil through the composting process. Here are some examples:
- Food waste: Fruit and vegetable scraps, eggshells, coffee grounds, and tea bags
- Yard waste: Grass clippings, leaves, and small twigs
- Paper products: Uncoated paper products like newspapers, paper bags, and cardboard
- Wood products: Small wood chips and sawdust can be composted, but it’s important to avoid wood that has been treated with chemicals.
- Plant-based plastics: Some types of biodegradable and compostable plastics made from plant materials like corn starch, sugar cane, or cellulose
- Natural fibers: Natural fibers like cotton, wool, and hemp
- Animal manure: Manure from cows, horses, chickens, and other farm animals
It’s important to note that not all compostable materials are suitable for all composting systems. For example, some industrial composting facilities may not accept food waste or animal manure, while others may require specific types of compostable plastics. It’s important to research the specific composting requirements and regulations in your area before adding materials to your compost pile or using compostable products.
5. Recyclable Steel Symbol
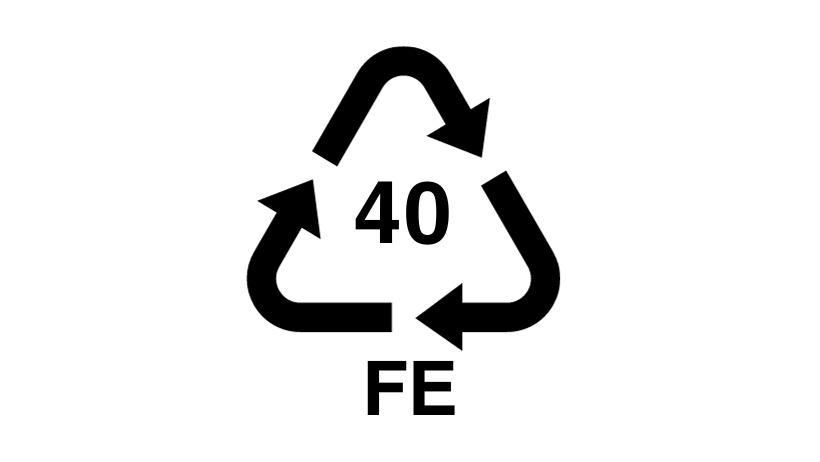
Recyclable steel refers to steel that can be recycled and reused in the production of new steel products. Steel is one of the most widely recycled materials in the world, with a recycling rate of around 90% in North America and Europe.
As a durable and strong material, a wide range of products, including cars, appliances, construction materials, and packaging use steel components. When steel products reach the end of their useful life, they can be collected and processed at recycling facilities to recover the steel and use it as a raw material for new products.
What does the Recyclable Steel Symbol mean?
The recyclable steel symbol is a logo that indicates that a product or packaging is made from recyclable steel. The symbol features a stylized triangle with the letters “Fe” inside, which is the chemical symbol for iron, the primary component of steel.
The symbol is used to help consumers identify products, and encourage them to properly dispose of steel products in recycling bins or at recycling facilities. By recycling steel, businesses can reduce their environmental impact, conserve natural resources, and support the circular economy.
6. Glass Recycling Symbol

Glass is a highly recyclable material that can be recycled indefinitely without losing quality or purity. Recycling glass conserves natural resources, reduces energy consumption, and prevents glass waste from ending up as litter or in landfills.
The process of glass recycling typically involves the following steps:
- Collection: Glass waste is collected from homes, businesses, and other sources and transported to a recycling facility.
- Sorting: Glass is sorted by color and type (such as clear, green, or brown) to ensure that only compatible glass is processed together. The sorting process removes non-glass materials, such as plastic or metal caps.
- Processing: The sorted glass is crushed into small pieces, called cullet, which are then melted in a furnace to create new glass products. To create the desired glass composition, processors mix raw materials, such as sand, soda ash, and limestone with the cullet.
- Manufacturing: Creators mold or blow into new products, such as bottles, jars, or glass fiber insulation.
Recycling glass has numerous environmental benefits. It reduces the need for virgin raw materials, such as sand and limestone, which can be environmentally damaging to extract. It also reduces energy consumption, as it requires less energy to melt and reform the cullet than to produce new glass from raw materials. Additionally, recycling glass helps to reduce waste in landfills, where glass can take thousands of years to decompose.
Sustainability Programs to Look For
Recycling programs around the world vary significantly in terms of their scope, effectiveness, and approaches. These programs play a crucial role in reducing waste, conserving resources, and mitigating environmental impact. Here are some examples of different recycling programs:
- Curbside Recycling Programs: Many municipalities offer curbside recycling, where residents can place recyclables like paper, cardboard, glass, and certain plastics in designated bins for collection.
- Deposit-Return Systems: Several countries implement deposit-return systems for beverage containers. Consumers pay a deposit when purchasing a drink in a specific container, and they can reclaim the deposit by returning the container to a designated collection point.
- E-Waste Recycling: E-waste recycling programs focus on safely disposing of and recycling electrical items like old computers, smartphones, and appliances to recover valuable materials and prevent environmental contamination.
- Composting Programs: These programs encourage the composting of organic waste, like food scraps and yard trimmings, to create nutrient-rich soil additives.
- Hazardous Waste Recycling: Some regions establish collection centers for hazardous materials such as batteries, fluorescent bulbs, and chemicals, preventing these substances from contaminating landfills.
- Textile Recycling: Programs aimed at reusing or recycling textiles divert clothing and fabrics from landfills and promote sustainable fashion practices.
- Community-Based Recycling: Initiatives like “Buy Nothing” groups and free stores promote sharing and reusing items within local communities.
- Waste-to-Energy Programs: Some areas employ waste-to-energy facilities that incinerate non-recyclable waste to generate electricity.
- Single-Stream Recycling: This approach simplifies recycling for residents by allowing them to place various recyclables into a single bin for recycling centers to sort later.
- Upcycling Initiatives: Creative programs encourage individuals and artisans to upcycle, turning discarded items into valuable products.
Keep in mind that recyclability can also depend on the condition of the item. If a recyclable item is notably dirty, damaged, or has food scraps, the recycling facility may not accept it. To avoid this possibility, do your best to clean out items before recycling.
These diverse recycling programs address different aspects of the waste stream. Each program contributes to the global effort to reduce waste and conserve resources while promoting environmental sustainability. The success of each program often depends on public participation, efficient infrastructure, and government policies.
Making it count
Understanding your recycling labels and the recycling process is a great step to reducing waste going to landfills. No matter what the symbol, check with your local recycling facility or recycling experts to ensure proper disposal. Get to know their specific guidelines and then adjust your recycling practices accordingly.
Looking to recycle e-waste or for a prepaid recycling program? CheckSammy can help. Contact us to learn about our on-demand recycling services.
See Our Services
Create a custom solution to meet your waste and sustainability goals. Contact us today!
Continue reading
Dive deeper into the CheckSammy Blog by reading one of our posts below
Feeling the Pain of Higher Resident Turnover? Apartment Junk Removal Can Help
If you’re a property manager, you’ve probably had a significant increase in tenant turnover over the last couple of years. So it’s no wonder apartment junk removal may be top of mind for you right now. There are several reasons for this shift. For one, the housing market is on fire right now. In 2020 […]
Read More About Feeling the Pain of Higher Resident Turnover? Apartment Junk Removal Can HelpSetting Up a Community E-waste Recycling Program
E-waste is the fastest-growing municipal waste stream according to the EPA, yet e-waste recycling isn’t keeping pace. In fact, only 12.5% of all e-waste is recycled, reports the EPA. Starting a community e-waste recycling program is a terrific way to ensure hazardous e-waste, like lithium-ion batteries, doesn’t end up in your community’s landfill. Creating an […]
Read More About Setting Up a Community E-waste Recycling ProgramWaste Management’s Role in the Circular Economy
Establishing a waste management program for your business or community is one of the best ways you can contribute to the circular economy. Here’s everything you need to know about waste management’s role in the circular economy (and how to get involved). What Is the Circular Economy? Our current economic model is all about taking […]
Read More About Waste Management’s Role in the Circular Economy5 Reasons to Consider a Textile Recycling Program for Your Organization
Americans sent more than 17 million tons of textiles to landfills in 2018, a volume that is only increasing every year, reports the Environmental Protection Agency. When you think about the fact that it can take over 200 years for textiles to decompose, it’s easy to grasp how large textile waste’s contribution is to the […]
Read More About 5 Reasons to Consider a Textile Recycling Program for Your Organization8 Benefits of Environmentally Friendly Power Washing Services
If you’re into maintaining the curb appeal of your business or home, then you’ve probably heard of pressure washing. Pressure cleaning involves using high-pressure water spray to remove grime, mold, dust, paint, mud, and other junk from objects or surfaces. Many people worry that pressure washing isn’t good for the environment, but this couldn’t be […]
Read More About 8 Benefits of Environmentally Friendly Power Washing ServicesWhy Our Customers Love Our Full-Service Junk Removal
If you’re looking for full-service junk removal services, you’ve come to the right place. CheckSammy is a one-stop shop for all your junk removal and sustainability needs. From our affordability, simplicity, and unrivaled turnaround times to our innovative sustainability solutions and patented technology and data, it’s clear why some of North America’s biggest companies choose […]
Read More About Why Our Customers Love Our Full-Service Junk RemovalTips for a Stress-Free Move From An Eco-Friendly Junk Removal Company
What does an eco-friendly junk removal company know about moving? Quite a lot, actually. Moving can be an especially chaotic time. You have to pack everything up, get rid of unwanted items, clean your property, load everything up, and move your things to your new location. That doesn’t even include the unpacking and resettling period. […]
Read More About Tips for a Stress-Free Move From An Eco-Friendly Junk Removal CompanyCollege Junk Removal Tips for Student Move-In Day
As the new school year gears up, colleges across the country are looking for ways to clean up their campuses before the new year begins, and many of them want to do so sustainably. College junk removal isn’t easy, though, especially around move-in week—and when trying to do so sustainably. As students move in and […]
Read More About College Junk Removal Tips for Student Move-In Day8 Items Hospitality Businesses May Not Know They Can Recycle
One hotel guest produces 2.5 pounds of trash every single day. Just a single hotel room produces around one cubic yard of waste each month, which totals 200 gallons of waste per room every month. Most of this waste goes straight to the landfill, even though research shows that up to 60% of it is […]
Read More About 8 Items Hospitality Businesses May Not Know They Can Recycle












